Configuring NetID Filtering on KONA Gateways
NetID filtering allows a TEKTELIC KONA gateway to forward only LoRaWAN® packets that match authorized networks or devices.
This feature helps reduce backhaul traffic and prevent data from roaming or misconfigured devices—particularly valuable for gateways using metered cellular connections.
KONA gateways support two methods for configuring NetID filtering:
- Through KONA Element or KONA Core servers using the Bulk Configuration interface.
- Through LoRa Basics Station when connecting to third-party network servers such as AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN.
Each LoRaWAN® packet contains unique identifiers that can be used for filtering:
| Identifier | Description |
|---|---|
| NetID | 24-bit identifier assigned to LoRaWAN network providers by the LoRa Alliance. |
| DevAddr | 32-bit device address derived from the NetID. Used for uplink traffic. |
| JoinEUI | 64-bit Join Server identifier used during OTAA join requests. |
| DevEUI | 64-bit unique device identifier. |
KONA gateways support filtering both uplinks and join requests.
- DevAddr List – screens regular uplink packets.
- JoinReq List – screens join requests.
Note
For reliable operation, configure both DevAddr and JoinEUI/DevEUI rules for each device.
Filtering only one type may result in lost join requests or uplinks.
{"loraTrafficFilter": {
"devAddrList": [
{
"ruleId": 111,
"action": "ALLOW",
"start": "26000000",
"end": "26FFFFFF"
},
{
"ruleId": 222,
"action": "DENY",
"start": "00000000",
"end": "FFFFFFFF"
}
],
"joinReqList": [
{
"ruleId": 1001,
"action": "ALLOW",
"devEUI_Start": "0004A30B001CXXXX",
"devEUI_End": "0004A30B001CXXXX",
"joinEUI_Start":"70B3D57EDXXXXX",
"joinEUI_End": "70B3D57EDXXXXX"
}
]
}}
This JSON snippet can be applied to gateways managed through KONA Element/Core, or adapted for Basics Station configurations.
-
BSP version 7.1.2 or newer
-
Gateway software:
tektelic-gateway-bridge 1.9.4-r81or latertektelic-lora-hal 5.2.1-r5or later
-
The gateway and devices are already provisioned in KONA Element or KONA Core.
-
Gateway is online.
- Log in to the KONA Element or KONA Core web portal.
- Open the Gateway Groups tab and select the gateway(s) to update.
- Click CONFIGURATION → Apply Configuration.
- In the Add Configuration dialog, paste your NetID filter JSON configuration.
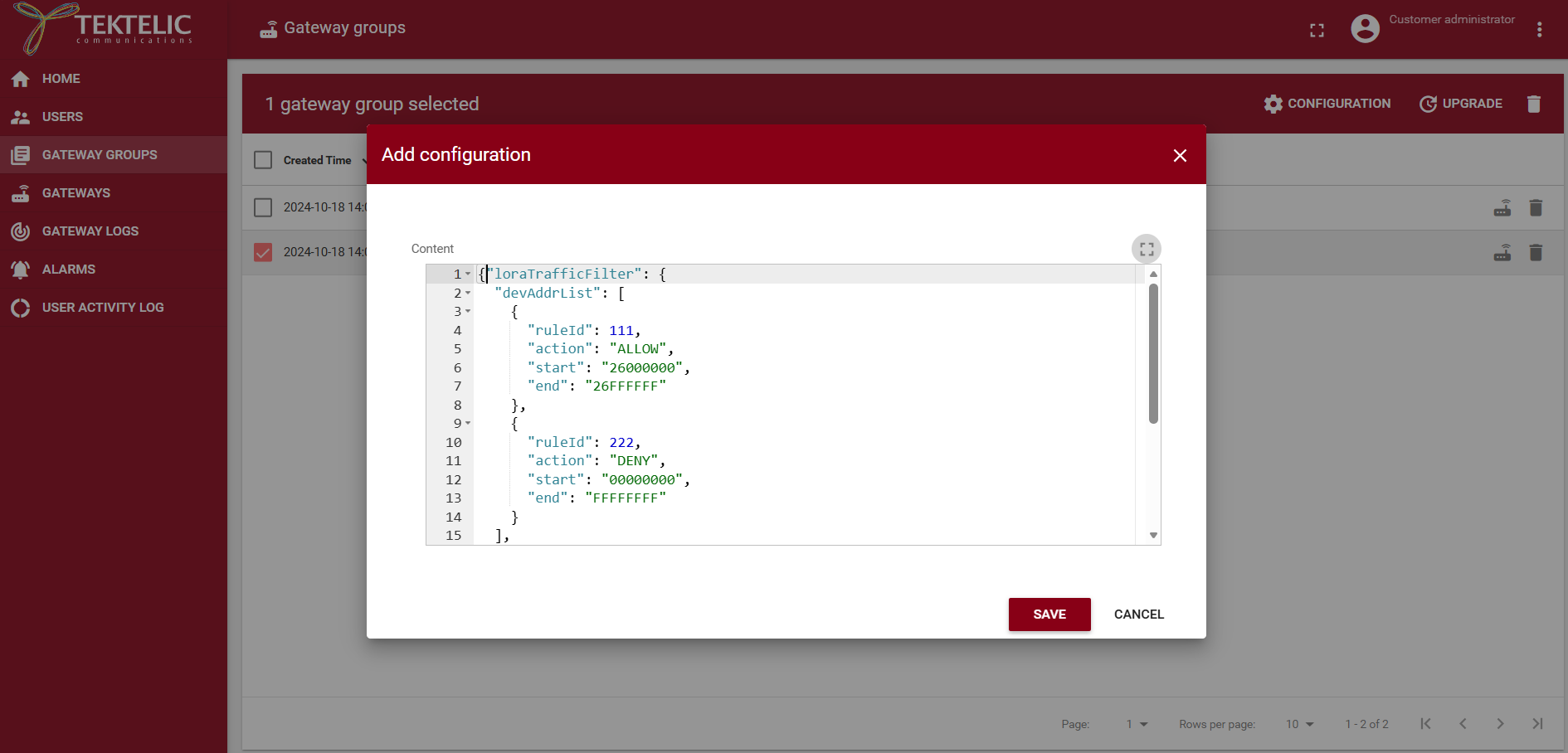
-
Click Save. The configuration is transferred to the gateway and saved locally.
-
To confirm, open CONFIGURATION → Get Configuration Status, select the gateway, and choose Get Configuration Status.
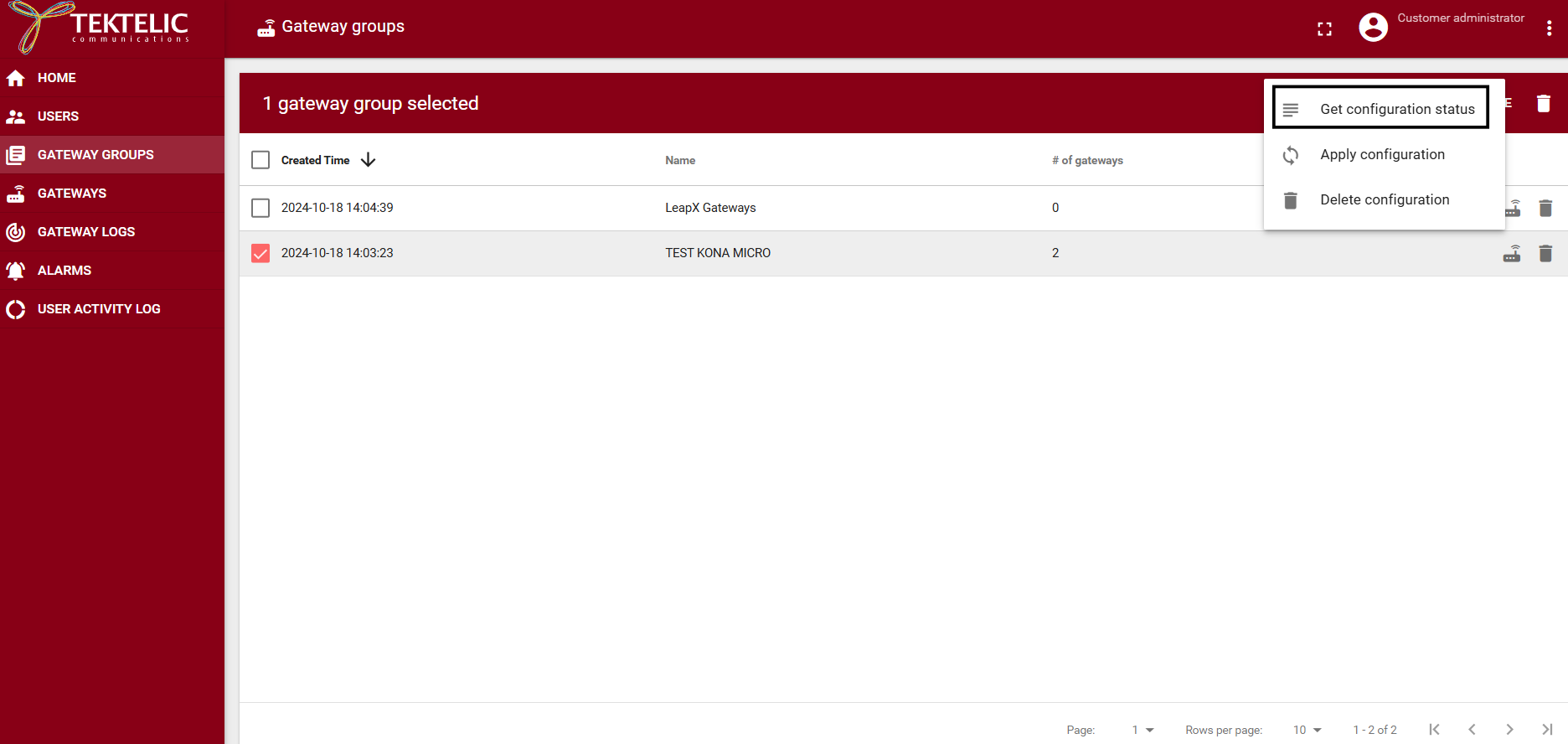
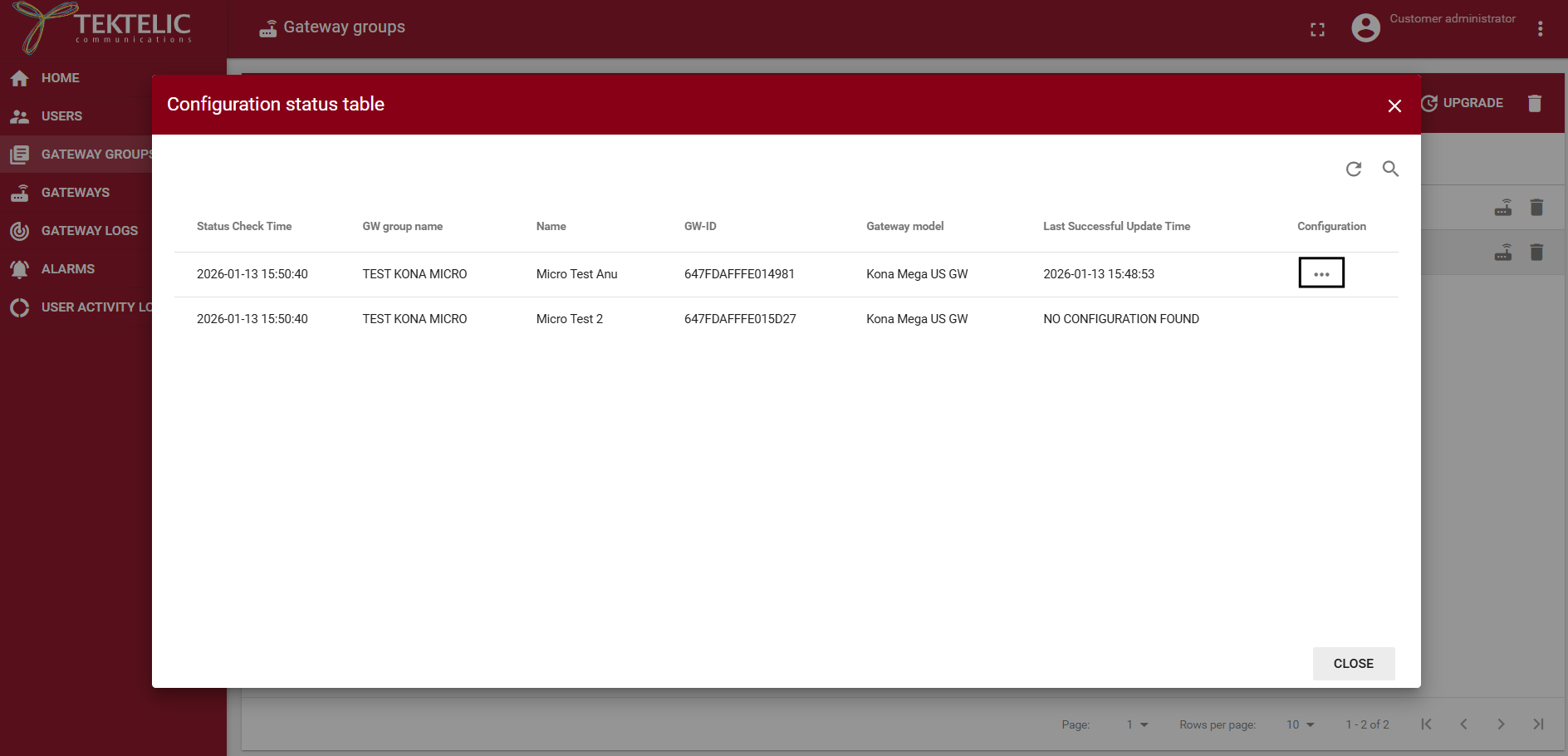
- Reboot each gateway to apply the new NetID filter.
When the gateway connects to a third-party network server via LoRa Basics Station, NetID filters are configured from the network server interface.
-
BSP version 7.1.2 or newer
-
Gateway software:
tektelic-bstn 1.9.4-r81or latertektelic-lora-hal 5.2.1-r5or later
-
Gateway registered and online in AWS IoT Core for LoRaWAN.
-
Sign in to the AWS IoT Console and open IoT Core for LoRaWAN.
-
Create a New gateway or Edit an existing gateway.
-
Expand LoRaWAN Configuration – optional.
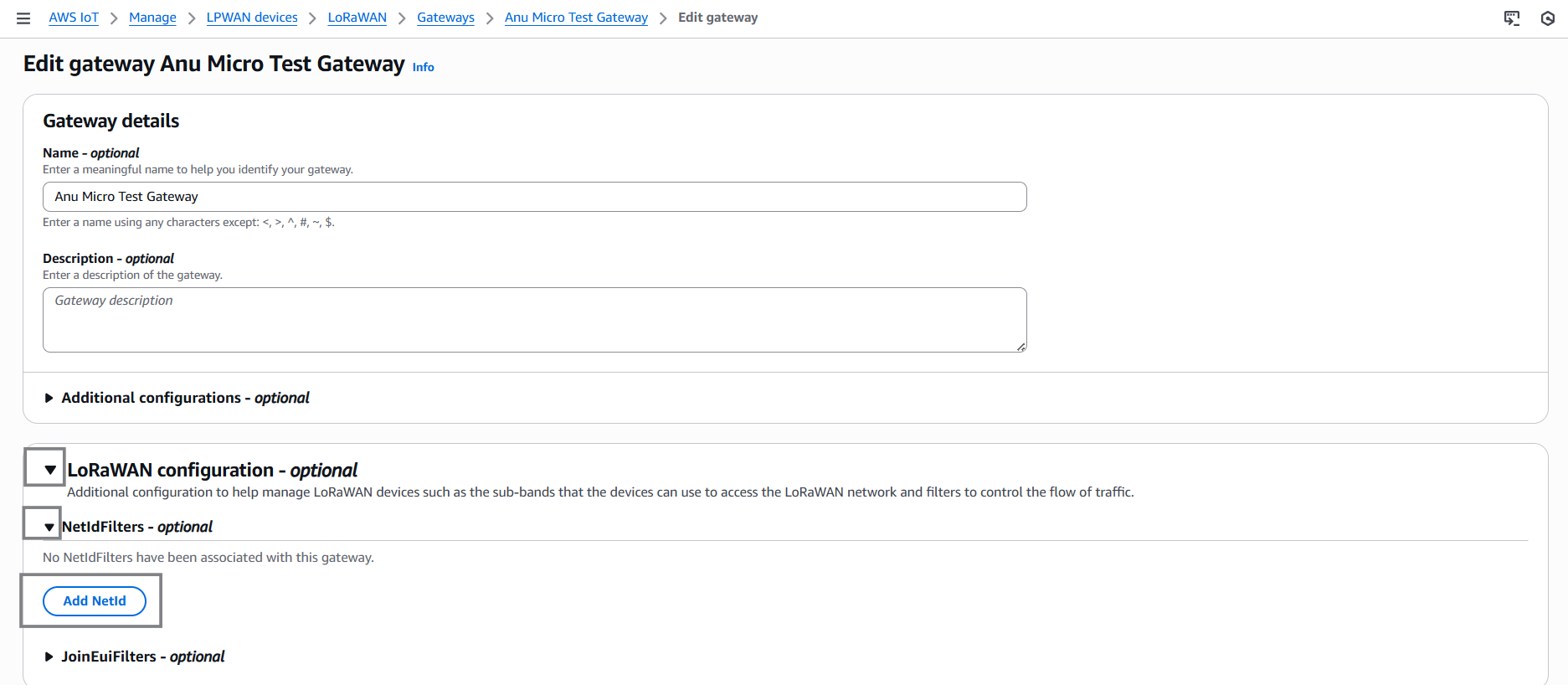
-
Under NetID Filters (optional), click Add NetID and enter the allowed NetID, for example:
000013
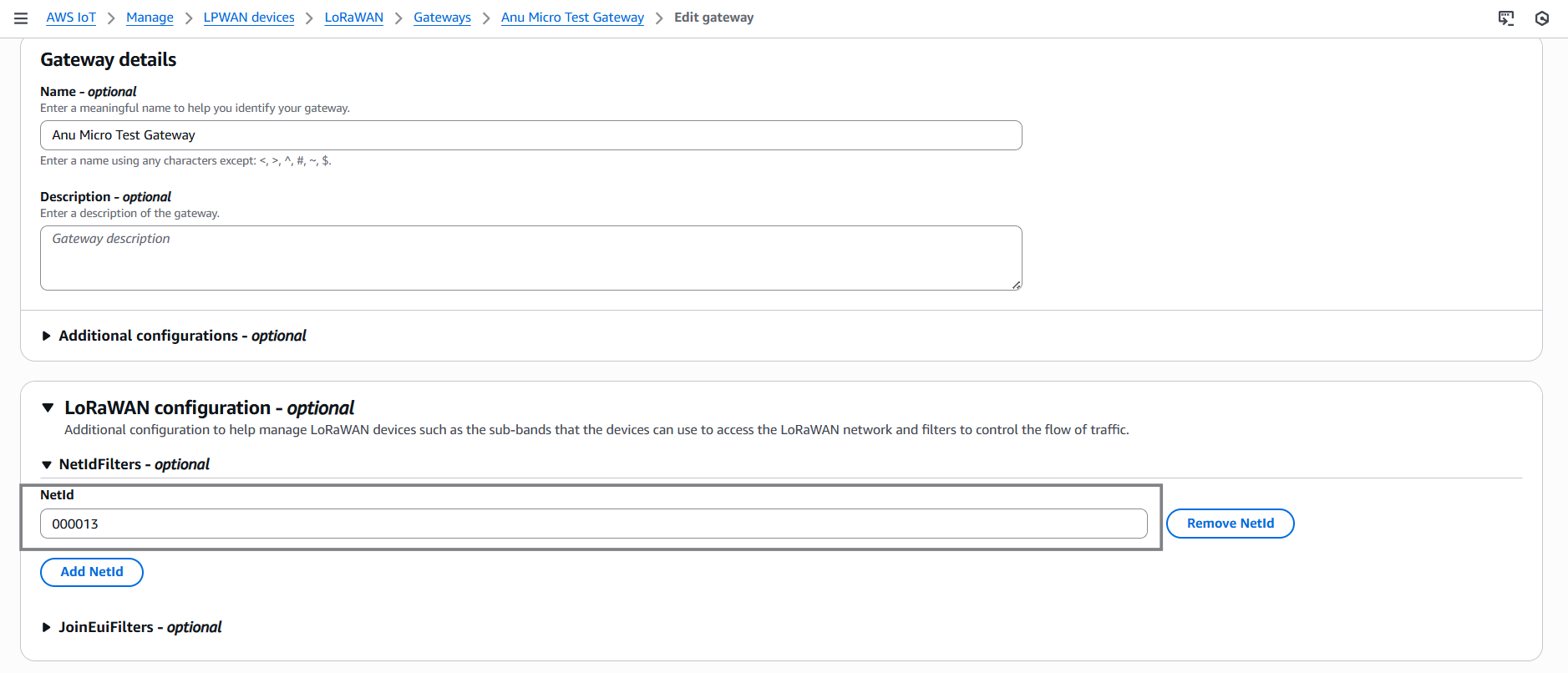
Refer to LoRa Alliance NetID Allocation page for NetID prefix https://lora-alliance.org/lorawan-network-coverage/
- (Optional) Add JoinEUI filters under JoinEUI Filters (optional).
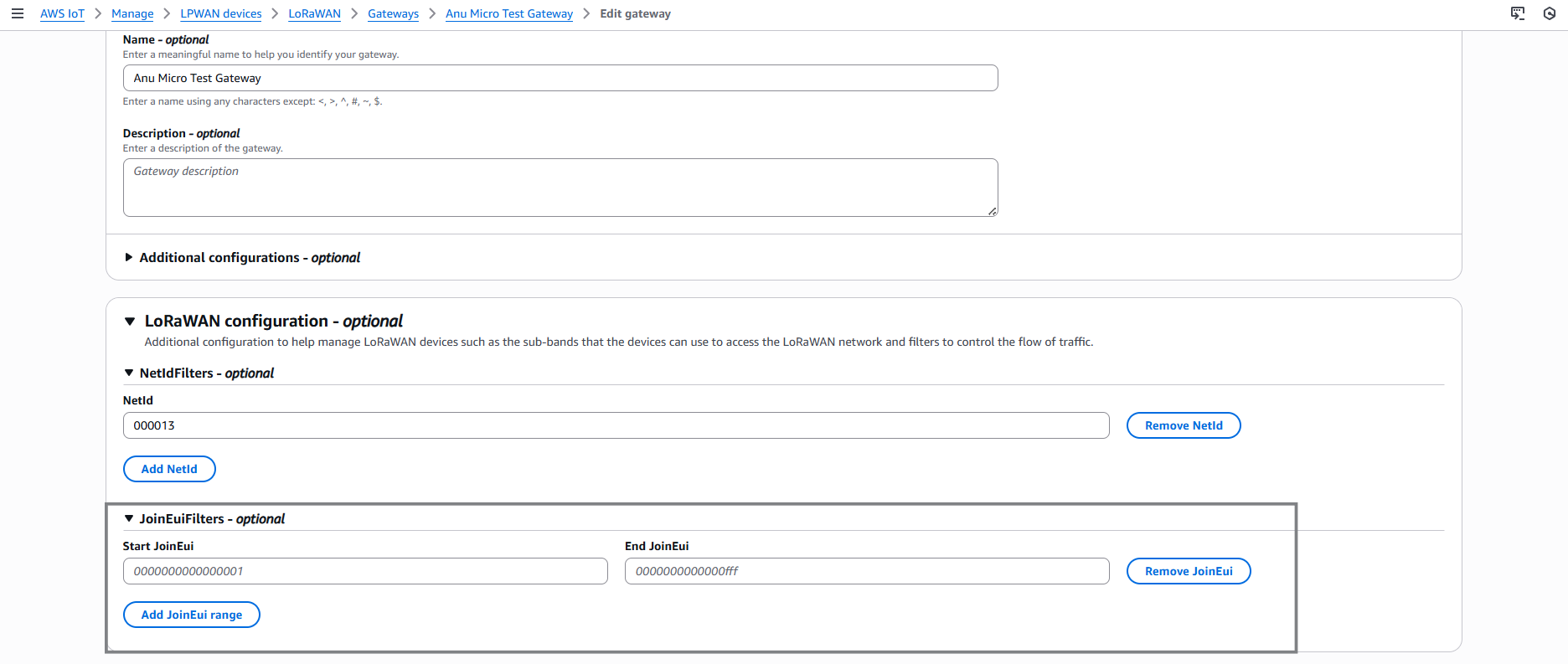
- Click Save. The gateway’s Basics Station service restarts automatically and applies the new filters.
Note AWS IoT Core filters only by NetID. DevAddr or JoinEUI range filtering is not supported.
| Configuration Method | Interface | Filter Types Supported | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| KONA Element / KONA Core | Bulk Configuration | DevAddr + JoinEUI/DevEUI | Managed gateways on TEKTELIC servers |
| Basics Station (AWS) | AWS IoT Console | NetID only | Third-party LNS integration |
- Verify that the gateway is online before applying the configuration.
- If the configuration fails to save, ensure your browser allows pop-ups or try Google Chrome.
- Always reboot the gateway after saving the configuration.
- Confirm successful filtering by reviewing the gateway’s uplink log entries.
